More info
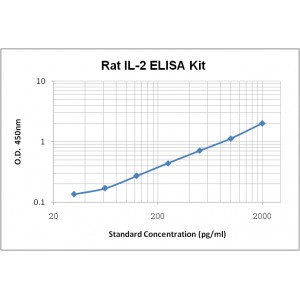
Assay Range | 31.2 - 2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Rat IL-2 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Rat IL-2 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 ml— 2
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Human Interleukin 2 (IL-2), also known as T cell growth factor (TCGF), is a member of the common gamma chain (γc) cytokine family. The 153 amino acid (aa) human IL-2 precursor contains a 20 aa signal sequence and a 133 aa mature region with one O-linked glycosylation site at Thr3 and three cysteines, two of which form an intra-chain disulfide bond that is essential for IL-2 bioactivity. The full-length rat IL-2 protein precursor is a 155 amino acid (aa) glycoprotein containing a 20 aa residue signal peptide and a 135 aa mature protein fragment. Mature rat IL-2 is approximately 80% identical to mouse IL-2. Human IL-2 shares approximately 60% sequence identity with mouse IL-2. IL-2 is expressed and secreted on γδT cells, activated conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, neurons, microglia, and hematopoietic stem cells in humans.
IL-2 first binds to IL-2 receptorα (IL-2Rα)/CD25 in the binary receptor complex then recruits IL-2Rβ/CD122 and IL-2Rγ/CD132 to trigger a variety of biological processes. IL-2 plays a key role in the development, maintenance and function of regulatory T cells and in promoting the development of activated CD8+ T cells into memory cells.