More info
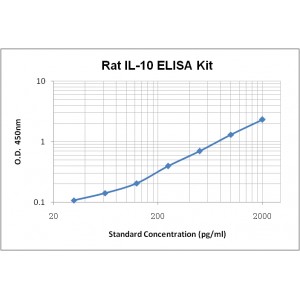
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 4.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Rat IL-10 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Rat IL-10 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), family of interleukin 1-theta (FIL1 theta), Interleukin-1 HY2 (IL-1HY2), Interleukin-1 theta (IL-1 theta) Interleukin-38 (IL-38), is a member of the IL-10 family. The 178 amino acid (aa) rat IL-10 precursor protein is composed of an 18 aa signal peptide and a 160 aa mature protein containing two potential N-linked glycosylation sites and five cysteine residues. Mature rat IL-10 shares 85% and 74% aa sequence identity with mouse and human IL-10, respectively. Rat and human IL-10 show species cross-reactivity on mouse cells, while mouse IL-10 is not active on human cells. IL-10 is secreted by activated hematopoietic cells, hepatic stellate cells, keratinocytes, and placental cytotrophoblasts.
IL-10 transduces its signals by binding to a heteromeric receptor complex composed of the type II cytokine receptor subunits IL-10 Rα/IL-10R1 and IL-10 Rβ/IL-10R2. The IL-10 dimer binds to two IL 10 Rα chains, and thus recruits two IL-10 Rβ chains and activates a signaling cascade involving JAK1, TYK2, and STAT3.IL-10 is a pleiotropic cytokine that plays positive and negative roles in immunoregulation and inflammation. It downregulates the expression of Th1 cytokines, MHC class II antigens, and co-stimulatory molecules on macrophages. It also enhances B cell survival, proliferation, and antibody production. It is reported that IL-10 is critical to the controlling of viral infections as well as allergic and autoimmune inflammation. Polymorphisms of IL-10 gene have been associated with the development of autoimmunity, viral infection, and cancer.