More info
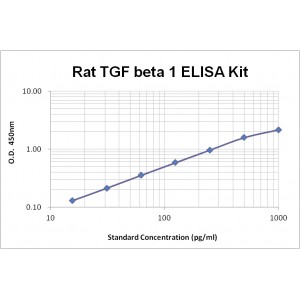
Assay Range | 15.6-1,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Rat TGF beta 1 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Rat TGF beta 1 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Transforming growth factor beta 1 or TGF-β1, encoded by TGFB1 gene in humans, is a secreted protein belonging to the TGF superfamily. The mouse and rat TGF-β1 are synthesized as a 390 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 29 aa signal peptide and a 361 aa pro-protein. Post-translation of TGF-β1 includes removal of the signal peptide and glycosylation of the pro-region. The glycosylation process contains the unusual attachment of mannose-6 phosphate residues and furin convertase-mediated cleavage of the prohormone, creating a 294aa disulfide-linked pro-region (termed LAP for latency-associated protein), and a 112aa disulfide-linked mature segment (termed TGF-β1). Interaction of these two peptides keeps TGF-β1 in an inactive state. To facilitate secretion and extracellular storage, a third 200 kDa component termed LTBP is covalently-linked to the N-terminus of one of the two LAP polypeptide chains. Mature mouse TGF-β1 shows 100% aa sequence identity to mature rat TGF-β1, and both rat and mouse TGF-β1 share 99% aa sequence identity with mature human TGF-β1.
The TGF-β1 receptor is a heterodimeric complex composed of a constitutively phosphorylated, ligand-binding glycoprotein (TβRII) and a signal-transducing, non-ligand-binding glycoprotein (TβRI/ALK-5). Data available suggested that TGF-β1 first binds TβRII which then phosphorylates TβRI and activates the downstream signaling pathways. In addition, a third TGF-β receptor may also be involved in TGF-β1 mediated cellular processes. TGF-β1 plays an important role in immunoregulation, cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. For example, it regulates dendritic cell chemotaxis by altering the expression of chemokine receptors. It can inhibit inflammatory response by dampening macrophage activity and proinflammatory secretion.