More info
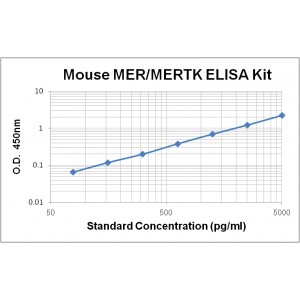
Assay Range | 78 - 5,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse MER standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse MER Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Mer, also known as tyrosine protein kinase Mer, proto-oncogene c-Mer, or receptor tyrosine kinase MerTK, is a member of the MER/AXL/TYRO3 receptor kinase family which is characteristic of two fibronectin type-III domains, two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains, and one tyrosine kinase domain. Mer is highly expressed in testis, ovary, prostate, lung, and kidney, and is also expressed in spleen, small intestine, colon, and liver at a lower level.
Mer is a receptor tyrosine kinase for several ligands including LGALS3, TUB, TULP1 or GAS6. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of Mer on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, Mer interacts with GRB2 or PLCG2 and induces phosphorylation of MAPK1, MAPK2, FAK/PTK2 or RAC1. Mer signaling plays a role in various biological processes such as macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells, platelet aggregation, cytoskeleton reorganization and engulfment. Mer also exhibits its inhibitory actions on Toll-like receptors (TLRs)-mediated innate immune response by activating STAT1, which selectively induces production of suppressors of cytokine signaling SOCS1 and SOCS3. Mutations in this gene have been associated with disruption of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) phagocytosis pathway and onset of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP).