More info
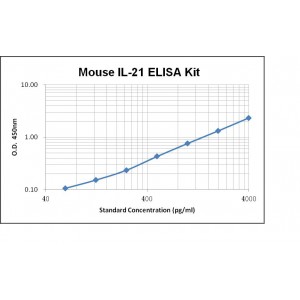
Assay Range | 62.5--4000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse IL-21 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate precoated with anti- Mouse IL-21 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL — 2
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1.
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1.
Background
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) is a cytokine encoded by the IL-21 gene in humans. IL-21 is produced by activated T follicular helper cells (Tfh), Th17 cells, and NKT cells. The mouse IL-21 is synthesized as a 155 amino acid (aa) precursor protein which consists of a predicted signal sequence and a mature chain. Mature mouse IL-21 shares 59% and 88% aa sequence identity with mature human and rat IL-21, respectively.
IL-21 elicits its biological activities by interacting with a heterodimeric receptor complex of the IL-21 specific IL-21R and the γc (common gamma chain) which is also a subunit of the receptors for IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15. In Tfh cells, IL-21 plays an important role in the development of humoral immunity through its autocrine effects on the Tfh cell and paracrine effects on immunoglobulin affinity maturation, plasma cell differentiation, and B cell memory responses. It is also required for the migration of dendritic cells to draining lymph nodes. It co-stimulates the activation, proliferation, and survival of CD8+ T cells and NKT cells and promotes Th17 cell polarization. It blocks the generation of regulatory T cells and their suppressive effects on CD4+ T cells. In addition, IL-21 suppresses cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions by limiting allergen-specific IgE production and mast cell degranulation. Dysregulation of the IL-21 signaling has been associated with the development of multiple immunological disorders.