More info
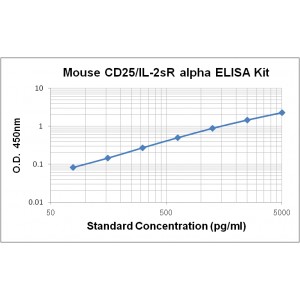
Assay Range | 78 - 5,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 5.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse CD25 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse CD25 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL-2 receptor subunit alpha, IL-2-RA, IL-2Rα, IL-2R subunit alpha, IL2-RA), also known as TAC antigen, p55 or CD25, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that binds to IL-2 and transduce the downstream signals in IL-2 activated cells. The mouse IL-2Rα is synthesized as a 272 amino acid (aa) precursor composed of a signal peptide, a extracellular domain (ECD) with two Sushi domains, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic domain. The ECD of mouse IL-2Rα shares 81% and 58% aa sequence identity with rat and human IL-2Rα, respectively.
The biological activities of IL-2 are mediated by its binding to a multi-molecular cellular receptor complex which is made up of 3 subunits - alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ). The α and β chains are required for binding IL-2, while signal transduction following IL-2 activation is carried out by the γ-chain and the β subunit. IL-2R β and IL-2Rγ are members of the type I cytokine receptor family, whereas IL-2Rα is structurally related only to the IL-15 Rα chain. A soluble form of IL-2Rα has been found in serum, concomitant with its increased expression on cells. The soluble form of IL-2Rα may be a poor inhibitor of IL-2 according to its low binding affinity. Increased levels of the soluble IL-2 Rα in biological fluids have been correlated with increased T and B cell activation and immune system activation.