More info
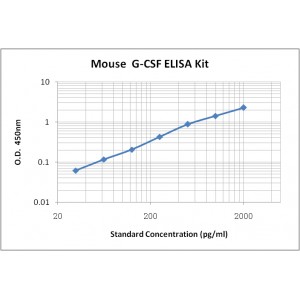
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 4.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse G-CSF standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse G-CSF Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF or GCSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF 3), is a glycoprotein belonging to the IL-6 superfamily. G-CSF is produced by activated monocytes and macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, astrocytes, neurons, and bone marrow stroma cells.Human and mouse G-CSF share 76% aa sequence identity and have species cross-reactivity.
G-CSF is produced by endothelium, macrophages, and a number of other immune cells. Alternative splicing of G-CSF transcripts generates two isoforms of G-CSF. The G-CSF receptor is present on precursor cells in the bone marrow. Interaction of G-CSF and the G-CSF receptor initiates proliferation and differentiation of the precursors into mature granulocytes. In the central nervous system, G-CSF functions as a neurotropic factor to induce neurogenesis, to increase the neuroplasticity and to counteract apoptosis. A recombinant form of G-CSF has been used in certain cancer patients to accelerate recovery from neutropenia after chemotherapy.