More info
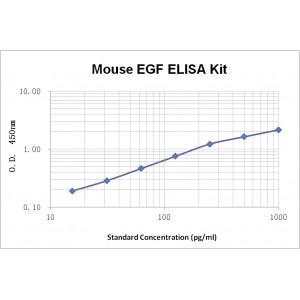
Assay Range | 15.6--1000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Sample Type | serum, plasma or cell culture supernatant |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse EGF standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse EGF Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is the founding member of the EGF family which structurally features the EGF-like domain characterized by three intramolecular disulfide bonds formed by six similarly spaced conserved cysteine residues. Except for EGF, this protein family also includes TGFα, amphiregulin (AR), betacellulin (BTC), epiregulin (EPR), heparinbinding,EGF-like growth factor (HBEGF), epigen, and the neuregulins (NRG)1- 6. The full-length 1207 amino acid (aa) human EGF precursor protein is a type I transmembrane protein that contains nine EGF domains and nine LDLR class B repeats. The 53 aa mature human EGF protein is proteolytically derived from removing the EGF domain proximal to the transmembrane region. Mature mouse EGF is 70% identical to mature human EGF. EGF is present in various body fluids, including blood, milk, urine, saliva, seminal fluid, pancreatic juice, cerebrospinal fluid, and amniotic fluid. Four ErbB (HER) family receptor tyrosine kinases including EGFR/ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4, are ligands for EGF family members. Depending on the context, EGF binds ErbB1 or ErbB2 to form homodimers or heterodimers of ErbB1/ErbB2. Dimerization leads to autophosphorylation of the receptor at specific tyrosine residues to create docking sites for a variety of signaling molecules. EGF plays an important role in epithelial development, angiogenesis, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, fibroblast proliferation.