More info
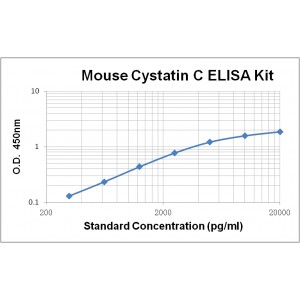
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse Cystatin C standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated withMouse Cystatin C Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Cystatin C, also known as neuroendocrine basic polypeptide, or post-gamma-globulin, is an extracellular cysteine protease inhibitor belonging to the cystatin superfamily. The cysteine proteases of the papain family, such as Cathepsins B, H, K, L, and S, are major targets of Cystatin C. Cystatin C forms reversible 1:1 complexes with its target enzymes in competition with their substrates. Mouse Cystatin C shares 72% and 88% aa sequence identity with human and rat Cystatin C, respectively. Cystatin C is produced ubiquitously and present in all biological fluids. It has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as inflammation and tumor metastasis. A single nucleotide mutation generating a replacement of Leucine 68 to glutamine in Cystatin C leads to hereditary Cystatin C amyloid angiopathy. Since Cystatin C also binds amyloid β and reduces its aggregation and deposition, it appears to be a potential target in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. On the other hand, Cystatin C levels have been reported to be higher in subjects with Alzheimer's disease. Cystatin C has also been used as an important biomarker for renal function assessment. Because of its small size and basic pI, Cystatin C is freely filtered by the glomerulus. It is then reabsorbed by tubular epithelial cells and subsequently metabolized so that it does not return to the bloodstream. Therefore, Cystatin C serum concentration correlates closely to the glomerular clearance rate.