More info
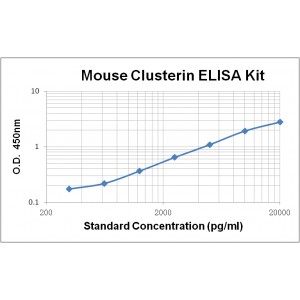
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse Clusterin standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated withMouse Clusterin Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Clusterin, also known as Apolipoprotein J, sulfated glycoprotein 2 (SGP-2), TRPM-2, Aging-associated gene 4 protein, and SP-40, is a secreted protein encoded by CLU gene in humans. Human Clusterin is synthesized as a precursor containing two coiled coil domains, three nuclear localization signals (NLS), and one heparin binding domain. Intracellular cleavages of the precursor remove the signal peptide and generate α and β chains to form disulfide-linked heterodimer. Mature mouse Clusterin shares 77% and 93% amino acid sequence identity with human and rat Clusterin, respectively. Clusterin is expressed primarily in adult testis, ovary, adrenal gland, liver, heart, brain, and in many epithelial tissues during embryonic development.
Clusterin binds a variety of molecules and functions as a chaperone of misfolded extracellular proteins. It is reported that high levels of Clusterin circulate predominantly as a component of high density lipoprotein particles which are internalized and degraded through interactions with LRP-2/Megalin. The ability of Clusterin to bind and neutralize non-oxidatively modified LDL reduces cytotoxicity in atherosclerotic plaques. Clusterin also is capable of reducing the accumulation of β-amyloid fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, it is shown that increased circulating levels of Clusterin enhance tumor aggressiveness by inhibiting apoptosis and by promoting the epithelial to mesenchymal transition.