More info
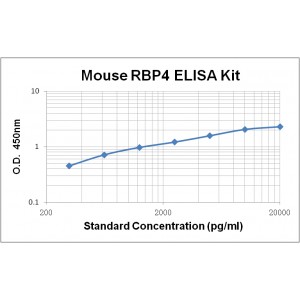
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse RBP4 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse RBP4 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4), also known as plasma retinol-binding protein (PRBP) belonging to the lipocalin superfamily. RBP4 is synthesized primarily by hepatocytes and adipocytes as a non-glycosylated, non-phosphorylated, and nonsulfated protein and is secreted into the blood in the presence of retinol. Proteolytic cleavage of RBP4 removes one or both C-terminal leucine residues to generate the 182 and 181 amino acid (aa) forms of RBP4. Mouse RBP4 shares 99.5% and approximately 85% aa sequence identity with rat and human counterparts, respectively.
RBP4 is a specific carrier for retinol (vitamin A alcohol) in the blood. It delivers retinol from the liver stores to the peripheral tissues. In plasma, the RBP-retinol complex interacts with transthyretin (TTR), which prevents its loss by filtration through the kidney glomeruli. The C-terminally processed forms of RBP4, which do not bind TTR, are normally excreted into the urine but accumulate in the serum during renal failure. In addition, RBP4 promotes hyperglycemia through downregulation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in adipocytes, upregulation of the hepatic gluconeogenic enzyme PEPCK, and attenuation of insulin receptor signaling in skeletal muscle. It is reported that serum RBP4 levels are elevated in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Polymorphisms within the RBP4 gene are also associated with increased serum levels and risk of type 2 diabetes.