Data sheet
| Specificity | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine. |
More info
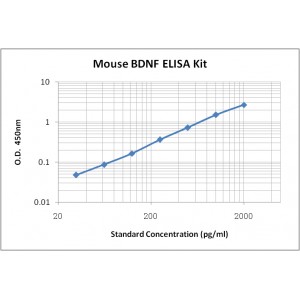
Assay Range | 31.2 - 2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 2.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reactions with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse BDNF standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse BDNF Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
BDNF, also known as Abrineurin, is a secreted protein belonging to the nerve growth factor. The full-length BDNF precursor is a 247 amino acid (aa) prepropeptide composed of an 18 aa signal peptide, a 110 aa prosequence, and a 119 aa mature segment. Reportedly, the N-terminus of the immature BDNF might be alternatively spliced, generating a longer pre-prosegment (pro-BDNF). The N-terminal pro-BDNF is removed by tPA and produce the 119 aa mature BDNF. BDNF is highly expressed in hippocampus, amygdala, cerebral cortex and cerebellum. It is also expressed in non-neuronal tissues such as heart, lung, skeletal muscle, testis, prostate and placenta. BDNF plays very important roles in a variety of biological processes of central and peripheral systems. During development, it promotes the survival and differentiation of selected neuronal populations. It is involved in axonal growth, pathfinding and in the modulation of dendritic growth and morphology. It regulates synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the brain. BDNF binds to the tyrosine kinase receptor (TrKB) and neurotrophin receptor (NTR) to transduce and mediate the downstream signaling cascades.
BDNF has been implicated in various pathological conditions of neurologic and/or mental disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, Rett syndrome, and dementia.synaptic function and long-term potentiation.