 View larger
View larger
Mouse High Mobility Group Box1 Protein HMGB1 ELISA Kit
BG-MUS11178
Mouse High Mobility Group Box1 Protein ELISA Kit
Data sheet
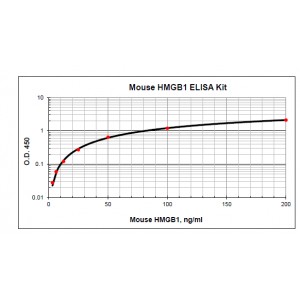
| Assay Range | 3.12 - 200 ng/mL |
| Storage | 2 - 8 ℃ |
| Expiration | 12 months |
| Assay principle | The Mouse HMGB1 ELISA Kit is based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Anti-Mouse HMGB1 specific antibody has been pre-coated onto 96-well plate. The test samples and the biotinylated goat anti-Mouse HMGB1 specific detection antibody are added to the wells subsequently and then followed by washing the plate. Streptavidin-HRP is added and unbound conjugates are washed away with Wash Buffer. HRP substrate TMB is used to visualize HRP enzymatic reaction. TMB is catalyzed by HRP to produce a blue color product that changes into yellow after adding acidic Stop Solution. The density of yellow is proportional to the amount of Mouse HMGB1 captured on plate. |
More info
| Precision | ||||||
| Intra-Assay Precision | Inter-Assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| CV (%) | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 10.6 |
| Average CV (%) | 4.9 | 9.6 | ||||
| Recovery | ||||||
| Standard Added Value | 12 - 100 ng/ml | |||||
| Recovery % | 93 - 105% | |||||
| Average Recovery % | 99% | |||||
| Linearity | ||||||
| Average Percentage of Expected Value (%) | ||||||
| Sample Dilution | Plasma | Serum | ||||
| 2 x | 104% | 97% | ||||
| 4 x | 103% | 98% | ||||
| 8 x | 99% | 96% | ||||
Citations:
1. S100B Promotes Glioma Growth through Chemoattraction of Myeloid-Derived Macrophages, Huaqing Wang, Leying Zhang, Ian Y. Zhang, Xuebo Chen, Anna Da Fonseca, Shihua Wu, Hui Ren, Sam Badie, Sam Sadeghi, Mao Ouyang, Charles D. Warden and Behnam Badie
Clin Cancer Res July 15 2013 (19) (14) 3764-3775; DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3725
2. Colon cancer cell treatment with rose bengal generates a protective immune response via immunogenic cell death, Jianzhong Qin et al, Cell Death & Disease, volume 8, page e2584 (2017)

