More info
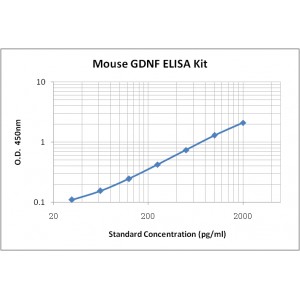
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse GDNF standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse GDNF Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a small protein belonging to the TGF-β superfamily. GDNF is a potent neurotrophic factor that promotes the survival of a series of neural cells, such as motoneurons, midbrain dopaminergic neurons, Purkinje cells and sympathetic neurons. Two alternative spliced variants of GDNF gene, referred to as astrocyte-derived trophic factors, have been described. Human GDNF is a 211 amino acid residue prepropeptide that is processed to yield a mature protein which exists in a homodimeric glycoprotein and is a ligand for the RET (rearranged during transfection) protein receptor. GDNF is expressed primarily in Sertoli cells, type 1 astrocytes, Schwann cells, neurons, pinealocytes and skeletal muscle cells. Mature human GDNF shares approximately 93% amino acid sequence identity with rat GDNF and exhibits species cross-reactivity in rat cells. GDNF is best known for its ability to support the survival of dopaminergic and motorneurons. These neuronal populations die in Parkinson's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The recombinant GDNF has been shown to promote the survival and differentiation of dopaminergic neurons in culture, and was able to prevent apoptosis of motor neurons induced by axotomy. Monkeys with an induced form of Parkinson's disease showed less trembling when treated with GDNF, suggesting that GDNF might be a potentially useful agent for Parkinson's disease therapy.