More info
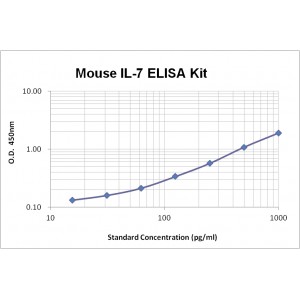
Assay Range | 15.6-1,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse IL-7 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with anti- Mouse IL-7 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a cytokine encoded by the IL-7 gene in humans. Mouse IL-7 is synthesized as a 177 amino acid (aa) precursor protein with a 25 aa signal peptide and a 152 aa mature protein containing essential disulfide bonds and multiple potential sites for N-linked glycosylation. Mouse IL-7 is approximately 60% aa sequence identity to mouse IL-7 and is equally active on both human and mouse cells. Although mouse IL-7 is active on human T cells, it was shown to be inactive on human pre-B cells.
IL-7 transduces its signals in target cells by binding to a receptor complex consisting of a ligand specific binding component, IL-7 Rα, and a second component, the γc (gamma common) chain, that is also a part of the receptor complexes involved in IL-2, IL-4, IL-9, and IL-15 binding and signal transduction. The Mouse IL-7 Rα is produced as a 459 aa precursor with a 20 aa signal peptide, a 219 aa extracellular domain, a 25 aa transmembrane domain, and a 195 aa cytoplasmic domain. IL-17 has exhibited multiple functions in various cell types. IL-7 can stimulate proliferation of B-lineage cells, pro-B and pre-B cells. It has been reported that IL-7 can induce proliferation of immature and mature human and mouse thymocytes, promote the generation of phenotypically mature CD45RA+ human thymocytes in vitro, and induce the V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor β gene in mouse fetal thymocytes. In the presence of co-mitogens such as Con A or PHA, IL-7 can stimulate the proliferation of peripheral blood T cells, support the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and promote the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells.