More info
|
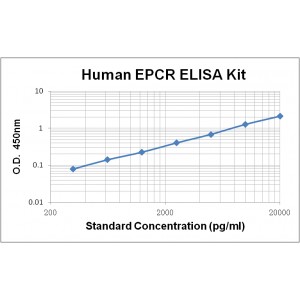
Assay Range |
312 -20,000 pg/mL |
|
Sensitivity |
10.0 pg/mL |
|
Size |
96T |
|
Storage |
Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
|
Assay Principle |
Sandwich ELISA |
|
Sample Volume |
100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
|
Detection Method |
Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human EPCR standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human EPCR Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), also known as activated protein C receptor (APC receptor), or CD201, is an N-glycosylated type I membrane protein encoded by the PROCR gene in humans. Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent serine protease involved in blood coagulation. Binding of Protein C to EPCR leads to the proteolytic activation of PAR1 (protease-activated receptor 1) on endothelial cells and subsequent upregulation of Protein C induced genes. EPCR enhances protein C activation by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Soluable form of EPCR derived from membrane bound EPCR by metalloproteolytic cleavage has been described. The extracellular domain of human EPCR shares approximately 61% amino acid sequence identity with mouse counterpart. EPCR is expressed primarily in the endothelial cells of arteries and veins in heart and lung. Clinically, Mutations in EPCR gene have been associated with venous thromboembolism and myocardial infarction, as well as with late fetal loss during pregnancy. In addition, it is shown that human EPCR functions as a receptor for subtypes of the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) family, suggesting that EPCR may be involved in Plasmodium falciparum malaria.
Citation:
Soluble endothelial protein C receptor and high sensitivity C reactive protein levels as markers of endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Their role in the prediction of vascular complications, Amal Zaghloul, et al, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, Volume 106, Issue 3, December 2014, Pages 597-604