More info
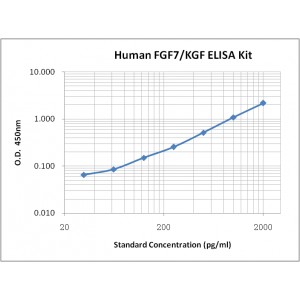
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 4.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human FGF7 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human FGF7 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Human Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF), also known as Fibroblast growth factor 7 (FGF-7), Heparin-binding growth factor 7 (HBGF-7), is a single chain, heparin-binding glycoprotein belonging to the fibroblast growth factor family. Mature KGF is a 163 amino acid (aa) protein containing five cysteines. KGF shows 29% and 38% aa sequence identity to FGF-2 and FGF-3, respectively. Expression of KGF has been observed in fibroblasts, embryonic mesenchymal cells, and smooth muscle cells.
The receptor for KGF (KGF R) is a restrictedly-expressed splice variant of the bek (bacterially expressed kinase) gene product, a cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase, also designated FGF R2 (FGF Receptor 2). FGF R2 is a full-length, unspliced type I transmembrane glycoprotein with an extracellular domain containing three Ig-like domains and a heparin-binding motif in the transmembrane domain. FGF R2 is expressed ubiquitously in connective tissue cells and binds FGF-1, FGF-2, and FGF-4 with high affinity. The KGF R differs from FGF R2 only within a 49 aa residue sequence found in the third Ig-like domain (D3). In addition to the KGF R, KGF also binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG). The significance of heparan sulfate for KGF binding and biological activity is currently unknown. In addition to its ability to induce cell proliferation, KGF may also promote epithelial differentiation. Cytokines such as IL-1(α and β) and IL-6 not only activate local connective tissue cells, resulting in foreign body clearance and tissue remodeling, but also stimulate the production of fibroblast KGF which contributes to re-epithelialization and wound closure.