More info
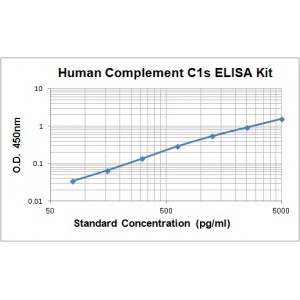
Assay Range | 78.1-5,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 78.1 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human C1s standard: 1 vial
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human C1s Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 30 mL - 1
4. HRP-antibody Conjugate (100x): 1 vial
5. TMB developing agent: 11 mL x2
6. Stop solution: 6 mL x1
7. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Complement represents one of the major effector systems for the immune responses. The classical complement pathway is triggered by C1, a complex composed of the binding protein C1q and two proenzymes, C1r and C1s. C1s proenzyme is a single chain 86,000 dalton protein that is the native form of C1s enzyme. C1s proenzyme is an inactive zymogen until C1 is activated. C1 complex binds to and is activated by antigen-antibody complexes (immune complexes) yielding C1r enzyme. C1r enzyme in the C1 complex activates C1s proenzyme generating C1s enzyme. As a highly specific serine protease, C1s executes the catalytic function of the C1 complex: the cleavage of C4 and C2, and thus initiates a sequence of activation steps of other components of the complement system, culminating in the formation of the membrane attack complex which induces cell lysis. Serpin C1, an inhibitor of serine protease, is the only other protein known to inhibits C1s activity and thus plays a regulatory role in controlling the function of C1s enzyme.