 The outbreak of a novel betacoronavirus (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCov) is a pandemic that resulted in almost 5 million lives loss by October, 2021. The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for urgently needed vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics. So far, S1 protein mRNA vaccine and protein vaccine have been used by several billions of...
The outbreak of a novel betacoronavirus (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCov) is a pandemic that resulted in almost 5 million lives loss by October, 2021. The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for urgently needed vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics. So far, S1 protein mRNA vaccine and protein vaccine have been used by several billions of...
 The outbreak of a novel betacoronavirus (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCov) is a pandemic that resulted in almost 5 million lives loss by October, 2021. The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for urgently needed vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics. So far, S1 protein mRNA vaccine and protein vaccine have been used by several billions of people.
The outbreak of a novel betacoronavirus (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCov) is a pandemic that resulted in almost 5 million lives loss by October, 2021. The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for urgently needed vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics. So far, S1 protein mRNA vaccine and protein vaccine have been used by several billions of people.
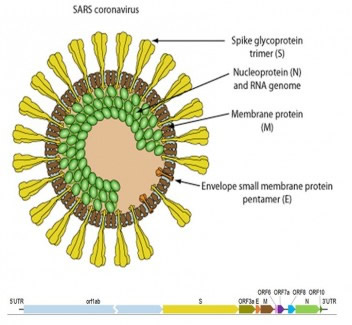
2019-nCoV/COVID-19/SARS-CoV2 makes use of a densely glycosylated, homotrimeric class I fusion spike (S) protein to gain entry into host cells. The S protein exists in a metastable prefusion conformation that undergoes a dramatic structural rearrangement to fuse the viral membrane with the host cell membrane. This process is triggered by binding of the S1 subunit to a host-cell receptor ACE2, which destabilizes the prefusion trimer, resulting in shedding of the S1 subunit and transition of the S2 subunit to a highly stable postfusion conformation. In order to engage a host-cell receptor, the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of S1 undergoes hinge-like conformational movements that transiently hide or expose the determinants of receptor binding. These two states are referred to as the “down” conformation and the “up” conformation, where “down” corresponds to the receptor-inaccessible state and “up” corresponds to the receptor-accessible state, which is thought to be less stable.
Antigens
Spike protein S1 S1-RBD Nucleoprotein ACE2
Antibodies
COVID-19 Spike Protein Antibody COVID-RBD antibody
ELISA kits
ACE2 ELISA SARS-CoV-2 RBD neutralization IgG titer ELISA, S1 antigen ELISA pair S1-RBD antigen ELISA pair RBD IgM ELISA RBD IgG ELISA NP antigen ELISA pair
Rapid Test (Lateral Flow) and PCR kit
COVID-19 Rapid Test for blood samples COVID-19 MaxSen One-Step RT-qPCR Kit
Publications:
1. Croci, G.A.; Vaira, V.; Trabattoni, D.; Biasin, M.; Valenti, L.; Baselli, G.; Barberis, M.; Guerini Rocco, E.; Gregato, G.; Scandroglio, M.; et al. Emergency Lung Transplantation after COVID-19: Immunopathological Insights on Two Affected Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ cells10030611
2. Suresh Gangadevi, Vishnu Nayak Badavath, Abhishek Thakur, Na Yin, Steven De Jonghe, Orlando Acevedo, Dirk Jochmans, Pieter Leyssen, Ke Wang, Johan Neyts, Tao Yujie, and Galia Blum. Kobophenol A Inhibits Binding of Host ACE2 Receptor with Spike RBD Domain of SARS-CoV-2, a Lead Compound for Blocking COVID-19. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2021 12 (7), 1793-1802 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03119.
3. Daniel P. Collins, Mark J. Osborn, Clifford J. Steer. Differentiation of immortalized human multi-lineage progenitor to alveolar type 2-like cells: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression and binding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike and spike 1 proteins. Cytotherapy, 000 (2021) 1-10.
2019-nCov/COVID-19 There are 31 products.
-
-
-
-
-
SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid ( 422a.a )...
DescriptionThe Recombinant SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid Protein is manufactured with N-terminal fusion HisTag. The Recombinant SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid His-Tagged Fusion Proteinis 47.8 kDa containing 422 amino acid residues of the SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid protein
$193.00In Stock -
-
-
-
-
-
-