More info
Overview
Long Name | Antibody Type | Antibody Isotype | Host | Species Reactivity | Validated Applications | Purification |
| ABL proto-oncogene 1, non-receptor tyrosine kinase | Polyclonal | IgG | Rabbit | Human, Rat | WB | Immunogen affinity purified. |
Immunogen | ||||||
| A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminus of human c Abl (1020-1049aa ERIASGAITKGVVLDSTEALCLAISRNSEQ), different from the related mouse sequence by one amino acid. | ||||||
Properties
Form | Lyophilized |
Size | 100 µg/vial |
Contents | Antibody is lyophilized with 5 mg BSA, 0.9 mg NaCl, 0.2 mg Na2HPO4, 0.05 mg NaN3. *carrier free antibody available upon request. |
Concentration | Reconstitute with 0.2 mL sterile dH2O (500 µg/ml final concentration). |
Storage | At -20 °C for 12 months, as supplied. Store reconstituted antibody at 2-8 °C for one month. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20 °C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
Additional Information Regarding the Antigen
Gene | ABL1 |
Protein | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 |
Uniprot ID | P00519 |
Function | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays a role in many key processes linked to cell growth and survival such as cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, cell motility and adhesion, receptor endocytosis, autophagy, DNA damage response and apoptosis. Coordinates actin remodeling through tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins controlling cytoskeleton dynamics like WASF3 (involved in branch formation); ANXA1 (involved in membrane anchoring); DBN1, DBNL, CTTN, RAPH1 and ENAH (involved in signaling); or MAPT and PXN (microtubule-binding proteins). Phosphorylation of WASF3 is critical for the stimulation of lamellipodia formation and cell migration. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and motility through phosphorylation of key regulators of these processes such as BCAR1, CRK, CRKL, DOK1, EFS or NEDD9. Phosphorylates multiple receptor tyrosine kinases and more particularly promotes endocytosis of EGFR, facilitates the formation of neuromuscular synapses through MUSK, inhibits PDGFRB-mediated chemotaxis and modulates the endocytosis of activated B-cell receptor complexes. Other substrates which are involved in endocytosis regulation are the caveolin (CAV1) and RIN1. Moreover, ABL1 regulates the CBL family of ubiquitin ligases that drive receptor down-regulation and actin remodeling. Phosphorylation of CBL leads to increased EGFR stability. Involved in late-stage autophagy by regulating positively the trafficking and function of lysosomal components. ABL1 targets to mitochondria in response to oxidative stress and thereby mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. ABL1 is also translocated in the nucleus where it has DNA-binding activity and is involved in DNA-damage response and apoptosis. Many substrates are known mediators of DNA repair: DDB1, DDB2, ERCC3, ERCC6, RAD9A, RAD51, RAD52 or WRN. Activates the proapoptotic pathway when the DNA damage is too severe to be repaired. Phosphorylates TP73, a primary regulator for this type of damage- induced apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspase CASP9 on 'Tyr-153' and regulates its processing in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Phosphorylates PSMA7 that leads to an inhibition of proteasomal activity and cell cycle transition blocks. ABL1 acts also as a regulator of multiple pathological signaling cascades during infection. Several known tyrosine-phosphorylated microbial proteins have been identified as ABL1 substrates. This is the case of A36R of Vaccinia virus, Tir (translocated intimin receptor) of pathogenic E.coli and possibly Citrobacter, CagA (cytotoxin- associated gene A) of H.pylori, or AnkA (ankyrin repeat-containing protein A) of A.phagocytophilum. Pathogens can highjack ABL1 kinase signaling to reorganize the host actin cytoskeleton for multiple purposes, like facilitating intracellular movement and host cell exit. Finally, functions as its own regulator through autocatalytic activity as well as through phosphorylation of its inhibitor, ABI1. |
Tissue Specificity | Widely expressed. |
Sub-cellular localization | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus. Mitochondrion . Note: Shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm depending on environmental signals. Sequestered into the cytoplasm through interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. Localizes to mitochondria in response to oxidative stress (By similarity). |
Sequence Similarities | Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. ABL subfamily. |
Aliases | Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Homolog 1 antibody|Abelson murine leukemia viral v abl oncogene homolog 1 antibody|Abelson tyrosine protein kinase 1 antibody|Abl 1 antibody| ABL antibody|Abl protein antibody|ABL proto oncogene 1 non receptor tyrosine kinase antibody|Abl1 antibody|ABL1_HUMAN antibody|bcr/abl antibody|Bcr/c abl oncogene protein antibody|c abl oncogene 1 non receptor tyrosine kinase antibody|c abl oncogene 1 receptor tyrosine kinase antibody|JTK 7 antibody|JTK7 antibody|p150 antibody|Proto oncogene tyrosine protein kinase ABL1 antibody|Proto-oncogene c-Abl antibody|Transformation gene oncogene ABL antibody|Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 antibody|v abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 antibody|v abl antibody |
Application Details
| Application | Concentration* | Species | Validated Using** |
| Western blot | 0.1-0.5μg/ml | Human, Rat | AssaySolutio's ECL kit |
AssaySolution recommends Rabbit Chemiluminescent WB Detection Kit (AKIT001B) for Western blot. *Blocking peptide can be purchased at $65. Contact us for more information

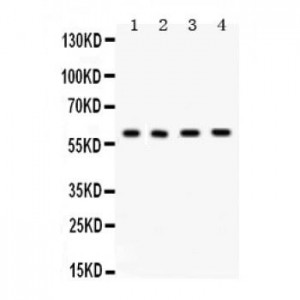
Anti- cABI antibody, ASA-B0247, Western blotting
All lanes: Anti cABI (ASA-B0247) at 0.5ug/ml
Lane 1: Rat Liver Tissue Lysate at 50ug
Lane 2: SMMC Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Lane 3: HELA Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Lane 4: PANC Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Predicted bind size: 55KD
Observed bind size: 60KD
All lanes: Anti cABI (ASA-B0247) at 0.5ug/ml
Lane 1: Rat Liver Tissue Lysate at 50ug
Lane 2: SMMC Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Lane 3: HELA Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Lane 4: PANC Whole Cell Lysate at 40ug
Predicted bind size: 55KD
Observed bind size: 60KD