Data sheet
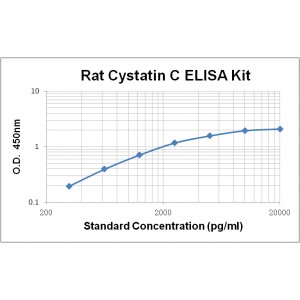
| Assay Range | 312-20,000 pg/ml |
More info
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Rat Cystatin C standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Rat Cystatin C Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Cystatin C, also known as neuroendocrine basic polypeptide, or post-gamma-globulin, is an extracellular cysteine protease inhibitor belonging to the cystatin superfamily. The cysteine proteases of the papain family are major targets of Cystatin C. Rat Cystatin C is a 120 amino acid (aa) protein, a glycosylated form of Cystatin C has been reported in rat, but not in mouse. Rat Cystatin C share 72% and 88% aa sequence identity with mouse and human Cystatin C, respectively. Cystatin C forms reversible 1:1 complexes with its target enzymes in competition with their substrates. Cystatin C is produced ubiquitously and present in all biological fluids. It has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as inflammation and tumor metastasis. A single nucleotide mutation generating a replacement of Leucine 68 to glutamine in Cystatin C leads to hereditary Cystatin C amyloid angiopathy. Since Cystatin C also binds amyloid β and reduces its aggregation and deposition, it appears to be a potential target in Alzheimer's disease. On the other hand, Cystatin C levels have been reported to be higher in subjects with Alzheimer's disease. Cystatin C has also been used as an important biomarker for renal function assessment. Because of its small size and basic pI, Cystatin C is freely filtered by the glomerulus. It is then reabsorbed by tubular epithelial cells and subsequently metabolized so that it does not return to the bloodstream. Therefore, Cystatin C serum concentration correlates closely to the glomerular clearance rate.