More info
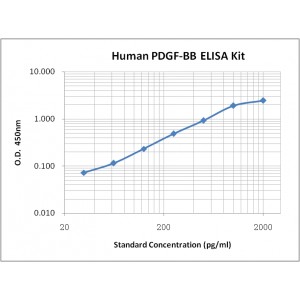
Assay Range | 31.2 - 2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Sample Type | serum, plasma, body fluids, tissue lysate or cell culture supernatant |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human PDGF-BB standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human PDGF-BB Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 ml— 2
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) represents a small group of proteins encoded by four distinct genes in which two genes (PDGF-C and -D) encode the CUB (C1r/Cls, Urchin EGF-like, and BMP1-1) domain, while the others (PDGF-A and -B) do not. PDGF-AB is the covalent heterodimer composed of the PDGF A and B chains. All PDGFs are synthesized as inactive propeptides that are further proteolytically processed to become active. Human PDGF-BB is a 241 amino acid (aa) preproprecursor composed of 20 aa signal sequence, a 61 aa N-terminal prodomain, a 109 aa mature region, and a 51 aa C-terminal prodomain. The proprecursor is initially dimerized and then intracellularly processed twice. The N-terminal domain (aa 21-81) is cleaved first, followed by cleavage of the C-terminal domain (aa 191-241). PDGF-BB is expressed by hepatocytes and non-resorbing osteoclasts, generating osteoblasts and bone formation. It is also produced by platelets, macrophages, and mast cells, and at sites of injury, promoting neutrophil and macrophage infiltration for debridement, fibroblast secretion of new ECM, and IFG-I mediated re-epithelialization.
Many different types of receptors are involved in PDGF-mediated signaling pathways. The classical receptor(s) for PDGF is proposed to be either a homodimer or heterodimer created from two type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases termed PDGF Rα and PDGF Rβ. In vitro studies indicated that the αα homodimer would bind PDGF-AA, -AB, -BB, and -CC, the αβ heterodimer would bind -AB, -BB and -CC, and the ββ homodimer would bind -BB and -DD. Other receptors that bind to PDGF include LRP1, FGFR1, neuropilin-1, and SorLA/LR11. PDGF-B is a growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. It is also a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin.