More info
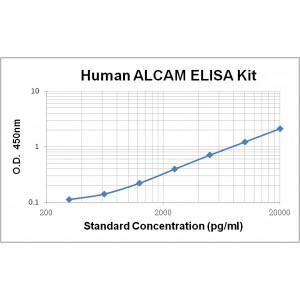
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human ALCAM standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human ALCAM Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
ALCAM (activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule), also known as CD166, MEMD and SC-1/DM-GRASP/BEN in the chicken, and KG-CAM in the rat, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the Ig CAM family of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Human ALCAM is synthesized as a 583 amino acid (aa) precursor protein composed of a 27 aa signal peptide, a 500 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with two V-type and three C2 -type Ig -like domains, a 22 aa transmembrane domain and a 34 aa cytoplasmic domain. A secreted isoform of ALCAM (sALCAM) has been described and is reported to be an antagonist of full-length ALCAM. ALCAM mediates low-affinity adhesion with itself or the cysteine-rich scavenger receptor CD6 to regulate T cell development, immunological synapses (IS), and cell migration through endothelial junctions. ALCAM on thymic epithelia mediates adhesion to CD6 on CD4+CD8+ T cells. Adhesion of ALCAM-expressing antigen presenting cells and CD6-expressing T cells stabilizes the early IS, while later it enhances CD3 effects on T cell proliferation, CD25 expression, and Th1 commitment. It is reported that ALCAM may influence expression or adhesion of the neuronal adhesion molecule NCAM-L1, both in the developing retina and invasive melanoma.