More info
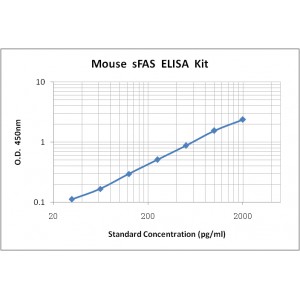
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 3.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Mouse sFAS standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Mouse sFAS Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Fas, also known as FAS receptor (FasR), apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1 or APT), cluster of CD95 or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 (TNFRSF6), is a glycoprotein belonging to the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily (TNFRSF). Fas is mainly expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes, and on malignant lymphoid cells. Fas is also expressed on cells from liver, heart, kidney, ovaries, and on many other malignant cells. Fas ligand (FasL), the physiological agonist for Fas, is also a transmembrane protein with homology to the TNF family in its extracellular domain. FasL is expressed primarily by activated T lymphocytes and by cells of the small intestine and lung. Five soluble Fas (sFas) proteins derived from alternatively spliced transcrpts of Fas gene have been detected in the supernatant of cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells or certain tumor cell lines. Interaction of FasL with Fas plays a very important role in initiating apoptotic signaling pathways. Mutations in Fas gene have been detected in humans with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Mice with mutations in either Fas or FasL exhibit accumulation of activated lymphocytes and classical autoimmune symptoms, suggesting that Fas-mediated apoptosis might primarily eliminate activated immune cells from the peripheral circulation.