More info
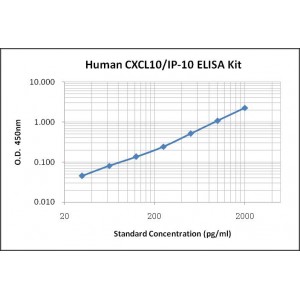
Assay Range | 31.2 - 2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human CXCL10 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human CXCL10 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL — 2
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
CXCL10 (C-X-C motif chemokine 10), also known as Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10) or small-inducible cytokine B10, is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family and a member of a subfamily of CXC chemokines that lacks the ELR (glutamic acid-leucine-arginine) motif. CXCL10 is expressed by activated T lymphocytes, neutrophils, splenocytes, keratinocytes, osteoblasts, astrocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. CXCL10 is induced in a variety of cells types including monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells in response to interferon-γ and LPS.
CXCR3 is a receptor for CXCL10, ITAC (CXCL11) and MIG (CXCL9). It is highly expressed in IL-2-activated T lymphocytes, eosinophils and CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells from human cord blood following GM-CSF stimulation. CXCR3 is constitutively expressed on neurons and neuronal processes in various cortical and subcortical regions of the brain. By binding to CXCR3, CXCL10 plays a role in the chemotaxis of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, NK, and NKT cells.
Clinically, CXC10 has been linked with numbers of disorders. Elevated levels of CXCL10 in the early and subclinical stage of Type I diabetes patients and in the salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome have been reported. It also has been found that CXCL10 was increased in the urine of patients with pulmonary diseases in the absence of renal dysfunction. CXCL10 may play a role in the pathogenesis of HIV infection. CXCL10 expression may be attributed to the accumulation of activated T cells in the cerebrospinal fluid compartment in HIV-1 infected individuals. Increased expression of CXCL10 has also been detected in astrocytes within the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Astrocytes expressing CXCL10 are commonly associated with senile plaques.