More info
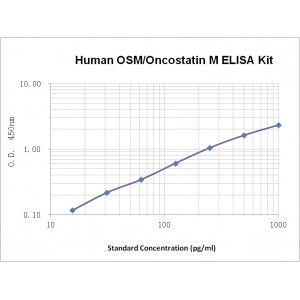
Assay Range | 15.6-1,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human OSM standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with anti-Human OSM Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1.
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1.
Background
Oncostatin M, also known as OSM, is a pleiotropic cytokine belonging to the interleukin 6 (IL-6) family in which it most closely resembles leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) structurally and functionally. The human OSM is synthesized as a 252 amino acid (aa) prepropolypeptide, composed of a 25 aa hydrophobic signal peptide, a 196 aa mature protein domain and a 31 aa hydrophilic C-terminal domain, that is proteolytically cleavable to generate the 196 aa mature form of OSM.
OSM initiates a series of biological processes in the target cells by interacting with a cell surface receptor complex of the type I receptor (gp130 and LIFR) and the type II receptor (gp130 and OSMR). gp130 serves as a low-affinity OSM receptor that does not transduce OSM signals, while the low affinity LIF receptor (LIFR) is a component of a high-affinity OSM receptor required for OSM signaling. OSM is also active on cells that do not express LIFR, suggesting that a specific OSM receptor exist. OSM has diverse functions in regulating cell growth. It inhibits the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines such as human A375 melanoma and mouse M1 myeloid leukemic cells. It stimulates proliferation of normal fibroblasts and AIDS-KS cells. It regulates production of IL-6, G-CSF and GM-CSF from endothelial cells. It plays a role in the maturation of fetal hepatocytes, as well as liver development and regeneration.