More info
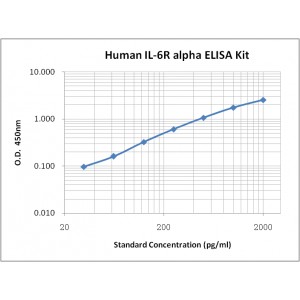
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human IL-6R alpha standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human IL-6R alpha Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a glycosylated cytokine which has exhibited multiple biological activities in various cells such as T cells, monocyte/macrophages, fibroblasts, hepatocytes, vascular endothelial cells, cardiac myxomas, bladder cell carcinomas, myelomas, astrogliomas, and glioblastomas. Basically, IL-6 plays a major role in the mediation of the inflammatory and immune responses initiated by infection or injury. For example, it stimulates B cell differentiation and antibody secretion; it acts as a co-stimulant with PHA or Con A to increase IL-2 production and IL-2 receptor expression by T cells; it enhances differentiation of cytotoxic T cells; it also acts as a growth factor for mature thymic or peripheral T cells, myelomas, hybridomas, plasmacytomas, keratinocytes, and mesangial cells. It is required for fever and the acute phase response in the liver, and it plays an important role in the transition from acute inflammation to either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease.
IL-6 elicits its activations by binding to a high-affinity receptor complex consisting of two membrane glycoproteins: an 80 kDa component receptor (IL-6 R) and a signal-transducing component of 130 kDa (gp130) that does not bind IL-6 by itself, but is required for high-affinity binding of IL-6 by the complex. IL6R, also termed CD126, IL-6R-alpha, or IL-6RA is a type I cytokine receptor which is characteristic of two fibronectin type-III-like domains to form a cytokine-binding domain and a WSXWS motif which is shown to be necessary for proper protein folding and thereby efficient intracellular transport and cell-surface receptor binding. IL-6R binds to IL-6 with low affinity, but does not transduce a signal.