More info
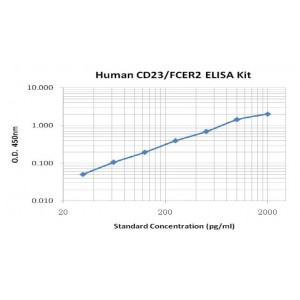
Assay Range | 31.2--2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 uLfinal volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human CD23 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human CD23 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 ml— 2
4. Detection antibody: 130 ul, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 ul, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
CD23, also known as Low affinity immunoglobulin epsilon Fc receptor, BLAST-2, C-type lectin domain family 4 member J, Fc-epsilon-RII, Immunoglobulin E-binding factor, Lymphocyte IgE receptor Fcε RII, is a member of the C-type lectin superfamily. It is a 47 kDa type II transmembrane glycoprotein containing a short N-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a transmembrane domain, an extracellular stalk region, and a C-terminal C-type (Ca2+-dependent) lectin domain. CD23 is a Low-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (IgE) and CR2/CD21. It plays essential roles in the regulation of IgE production and in the differentiation of B-cells. Two alternatively spliced isoforms (CD23a and CD23b) have been described. CD23a is constitutively expressed by B cells and intestinal epithelial cells (IEC). CD23b is induced on a variety of cell types including B cells, monocytes, eosinophils, IEC and airway smooth muscle cells by a range of exogenous stimuli, including IL-4 and GM-CSF. A series of soluble forms of CD23 (sCD23) generated by metalloproteinases (principally ADAM10) and cysteine proteases have also identified. On IEC, membrane CD23-mediated transepithelial transport of IgE/allergen complexes to the underlying mast cells is associated with food allergies. On B cells, CD23a complexed with HLA-DR and antigen-IgE, undergoes efficient endocytosis to enhance the IgE-dependent antigen presentation to T cells. On macrophages, CD23b mediates phagocytosis of IgE-opsonized particles. Binding of circulating IgE to membrane CD23 down-regulates further IgE production, while binding of most forms of soluble CD23 to CD21 up-regulates the level of IgE production by B cells. Soluble CD23 also binds αm/β2, αx/β2 and αv integrins on monocytic cells to activate production of inflammatory cytokines. Overexpression of CD23 and elevated levels of sCD23 has been implicated in certain pathological conditions, such as allergy, rheumatoid arthritis and B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL).