More info
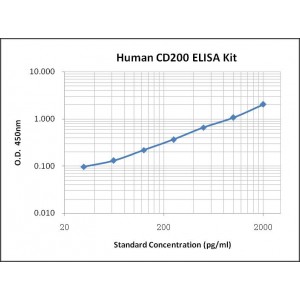
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human CD200 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human CD200 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
CD200, also known as OX-2 (OX-2 membrane glycoprotein), is a transmembrane immunoregulatory protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The human CD200 is a 278 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes a 30 aa signal sequence, a 202 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 27 aa transmembrane segment, and a 19 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD is composed of one Ig-like V type domain and one Ig like C2 type domain. Multiple alternatively spliced variants of CD200 have been described. The ECD of human CD200 shares 76% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat CD200.
CD200 is a ligand for CD200R which is expressed primarily in mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells, suggesting that CD200 may play an important role in myeloid cell regulation. It is reported that CD200 knockout mice are characterized by increased macrophage number and activation and are predisposed to autoimmune disorders. CD200 interacts with CD200R via their respective N-terminal Ig like domains. In myeloid cells, CD200R initiates inhibitory signals following ligand binding, while, in T cells, CD200 functions as a costimulatory molecule independent of the CD28 pathway. Several other CD200R- like molecules have been identified in human and mouse, but their capacity to interact with CD200 needs to be investigated further. Interestingly, many viruses encode CD200 homologs which are expressed on infected cells during the lytic phase. It is showed that viral CD200 homologs also suppress myeloid cell activity to increase viral propagation.