More info
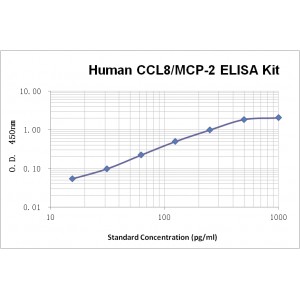
Assay Range | 15.6--1000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 1.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Sample Type | serum, plasma or cell culture supernatant |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human CCL8 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human CCL8 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
CCL8 (chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 8), also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (MCP-2), HC14 or small-inducible cytokine A8, is a small protein belonging to the CC chemokine family. The CCL8 gene encodes a 109 amino acid (aa) precursor containing a 34aa signal peptide and a 75aa mature protein. Mature human MCP-2 shares 62% and 58% amino acid sequence identity with MCP-1 and MCP-3, respectively. MCP-2 exhibits chemotactic activity in many different immune cells, including mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, T cells, and NK cells. CCL8 binds to several different cell surface receptors, such as CCR1, CCR2B and CCR5 to trigger a series of cellular processes. An N-terminal truncated form MCP-2(6-76), produced by proteolytic cleavage after secretion from peripheral blood monocytes, has lost monocyte chemotactic activity, but inhibits the chemotactic effect of CCL2, CCL5, CCL7 and CCL8.