More info
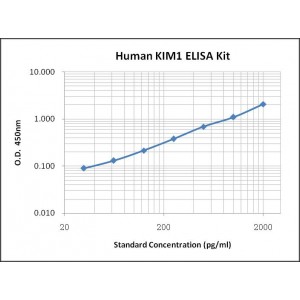
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Sample Type | serum, plasma, body fluids, tissue lysate or cell culture supernatant |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human KIM1 standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human KIM1 Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
T cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin domain 1 (TIM-1), also known as Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1) and Hepatitis A Virus Cellular Receptor (HAVCR), is a member of the TIM family. In humans, three TIM/KIM genes have been described. Human TIM-1 is synthesized as a 359 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 20 aa signal sequence, a 270 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane region, and a 48 aa cytoplasmic domain. Multiple TIM-1 variants can be derived from deletions in the mucin domain caused by polymorphisms or alternative splicing of HAVCR1 gene. The ECD of human TIM-1 shares 50% and 40% aa sequence identity with rat and mouse TIM-1, respectively. The expression of TIM-1 is upregulated on activated Th2 cells, after dendritic cell maturation, and on kidney tubular epithelial cells after injury. A soluble form of TIM-1 generated by proteolytical cleavage has been detected in the urine and in circulation. Urinary TIM-1 is highly elevated in nephropathy and may be a useful biomarker for renal damage.
It is reported that TIM-1 may be a receptor for a number of ligands, including phosphatidylserine, leukocyte mono- immunoglobulin-like receptor 5 (LMIR5/CD300b), TIM-4, IgA, and the glycoproteins of a number of enveloped viruses. In humans, TIM-1 serves as a cellular entry receptor for various viruses, including hepatitis A virus, Ebola-virus, and Marburg-virus. TIM-1 signaling co-stimulates T cell activation and enhances Th2 cytokine production. Interaction with phosphatidylserine enables TIM-1 to mediate the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. In TIM-1-bearing iNKT cells, interaction with apoptotic cells can also result in iNKT cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. Interactions between cell-surface or soluble TIM-1 with LMIR5 is proposed to induce LMIR5-mediated activation of myeloid cells including macrophages/monocytes, mast cells, neutrophils, and dendritic cells.