More info
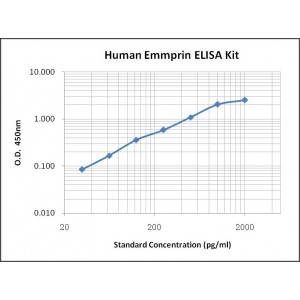
Assay Range | 31.2-2,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 2.0 pg/mL |
Specificity | No cross-reaction with other related substances detected |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human Emmprin standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human Emmprin Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN), also known as CD147, basigin, leukocyte activation antigen M6, collagenase stimulatory factor, tumor cell-derived stimulatory factor, and OK blood antigen, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Human EMMPRIN precursor is a 269 amino acid (aa) protein containing a 24 aa signal sequence, a 183 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with one C2-type and one V-type Ig-like fragments, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 41 aa intracellular domain. The full-length human EMMPRIN shows 58% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat EMMPRIN.
EMMPRIN is expressed in areas of tissue remodeling, including tumors, endometrium, placenta, skin, and regions undergoing angiogenesis. It is also expressed in lymphoblasts, macrophages, and tumor cells and is often co-expressed with the amino acid transporter CD98h. Interactions of EMMPRIN with CyPA (cyclophilin A) and CyP60 (cyclophilin C) promote leukocyte inflammatory chemotaxis and cell surface expression of EMMPRIN, respectively. EMMPRIN stimulates adjacent fibroblasts to produce matrix metalloproteinases (MMPS) and plays pivotal roles in spermatogenesis, embryo implantation, neural network formation and tumor progression. In addition, EMMPRIN is shown to induce urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), VEGF, hyaluronan, and multiple MMPs. Clinically, EMMPRIN has been shown to be up-regulated in gliomas. Levels of EMMPRIN expression correlate with malignant potential of the tumor.