More info
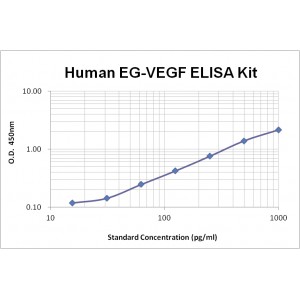
Assay Range | 15.6-1,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 7.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human EG-VEGF standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with anti- Human EG-VEGF Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor (EG-VEGF), also called prokineticin 1 (PK1), is a member of the prokineticin family characterized by a common structural motif of ten conserved cysteine residues forming five pairs of disulfide bonds. Members of this family include the mammalian EG-VEGF/PK1 and PK2, the venom protein A (VPRA) from the venom of black mamba snake and Bv8 from the frog Bombina variegate. Human EG-VEGF precursor is a 105 amino acid (aa) protein containg a 19 aa signal peptide and a 86 aa mature protein.
EG-VEGF binds to and activates two closely related G protein coupled receptors, EG-VEGF/PK1R1 and EG-VEGF/PK2R2 through which EG-VEGF initiates the activation of p44/p42 MAP kinase signaling pathways and promote phosphoinositide turnover. EG-VEGF is expressed in multiple tissues including the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and steroidogenic glands (testis, ovary, placenta and adrenal glands). Primarily, EG-VEGF potently stimulates the contraction of GI smooth muscle. In addition, EG-VEGF has been shown to induce proliferation, migration and formation of membrane discontinuities in capillary endothelial cells derived from endocrine glands. It is capable of promoting the proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma cells. EG-VEGF also is a tissue-specific angiogenic factor that exhibits biological activities similar to that of VEGF on selected cells.