More info
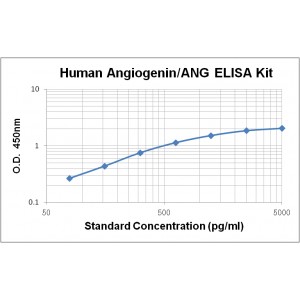
Assay Range | 78 - 5,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 12.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human Angiogenin standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human Angiogenin Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Angiogenin (ANG), also known as ribonuclease 5, is a small protein that is encoded by the ANG gene in humans. Angiogenin plays a key role in angiogenesis for normal and tumor growth. In smooth muscle and endothelial cells, ANG forms a complex with Actin to activate proteolytic cascades which degrade the laminin and fibronectin layers of the basement membrane by upregulating the production of proteases and plasmin. Degradation of the basement membrane and extracellular matrix allows the endothelial cells to penetrate and migrate into the perivascular tissue. ANG-mediated signaling pathways activate the downstream signaling molecules ErK1/2 and Akt which leads to invasion of the basement membrane and cell proliferation associated with further angiogenesis. In addition, ANG can enter into the nucleus in which it enhances rRNA transcription by binding to the CT-rich angiogenin binding element (ABE) in upstream intergenic region of rDNA to activate other angiogenic factors that induce angiogenesis. ANG is distinct from many other angiogenic proteins in that it has the same general catalytic properties as RNase A and cleaves preferentially on the 3' side of pyrimidines. Importantly, the ribonucleolytic activity of ANG is essential to its angiogenic activity. ANG has a prominent role in the pathogenesis of cancer due to its angiogenetic activity. ANG inhibition has been showed to be a promising strategy for cancer therapy.