More info
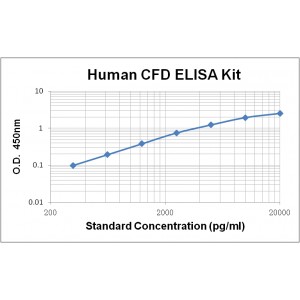
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human CFD standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human CFD Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
Complement factor D (CFD), also known as adipsin, C3 convertase activator, properdin factor D, is a serine protease that is required for the initiation of complement activation via the alternative pathway. Upon activation through reversible substrate-induced conformational change into an active enzyme, CFD functions to cleave the C3b-bound factor B, resulting in the formation of C3bBb complex, which is the alternative pathway C3 convertase. Human CFD is synthesized as a 253 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 20aa signal peptide, a five-residue activation-/pro-peptide, and the 228 aa mature chain. Physiologically, mature CFD lacking the activation peptide circulates as an inactive enzyme and requires interaction with its natural substrate, C3b-bound factor B, for activation of its catalytic activity. Mature human CFD shares 66% aa sequence homology with the mouse counterpart.
CFD is expressed in multiple tissues, including monocyte/macrophages, muscle, sciatic nerve, endometrium, kidney, intestine, and at especially high levels in adipocytes. It is reported that expression of CFD is reduced in various mouse models of obesity, suggesting that CFD might play a role in fat metabolism or systemic energy balance. Serum CFD is regulated through catabolism in the kidney where CFD is filtered by the glomerulus and reabsorbed by the proximal tubule. In patients with renal failure, circulating levels of CFD are usually elevated. CFD deficiency is associated with low activity of the alternative complement pathway and low capacity to opsonize bacteria. It is shown that, in patients with mutations in the CFD gene resulting in CFD deficiency, recurrent bacterial infections were observed.