More info
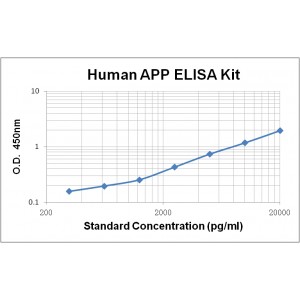
Assay Range | 312 -20,000 pg/mL |
Sensitivity | 10.0 pg/mL |
Size | 96T |
Storage | Store at 2 - 8ºC. Keep reconstituted standard and detection Ab at -20 ºC |
Assay Principle | Sandwich ELISA |
Sample Volume | 100 µL final volume, dilution factor varies on samples |
Detection Method | Chromogenic |
Kit Components
1. Recombinant Human APP standard: 2 vials
2. One 96-well plate coated with Human APP Ab
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 mL - 1
4. Detection antibody: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
5. Streptavidin-HRP: 130 µL, dilution 1:100
6. Antibody diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
7. Streptavidin-HRP diluent buffer: 12 mL x1
8. TMB developing agent: 10 mL x1
9. Stop solution: 10 mL x1
10. Washing solution (20x): 25 mL x1
Background
APP (Amyloid Precursor Protein), also known as Amyloid beta A4 protein, Alzheimer disease amyloid A4 protein homolog, or Amyloidogenic glycoprotein (AG), is a type I transmembrane protein composed of a 682 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with two heparin binding domains, a copper binding domain, a BPTI/Kunitz inhibitor domain, and a collagen binding domain, a 24 aa transmembrane segment, and a 47 aa cytoplasmic domain. APP is cleavable to generate a number of proteolytic fragments. In the non-amyloidogenic pathway, the APP ECD is cleaved by α-secretase (ADAM10) within the Amyloid β sequence to prevent the formation of Amyloid β peptides. APP can also be cleaved by β-secretase just N-terminal to the Amyloid β sequence to release a slightly shorter ECD fragment known as APPβ. Following this cleavage, the remaining portion of APP can be further proselytized by γ-secretase (a multi-subunit complex including Presenilin) whthin the transmembrane domain to generate the Amyloid β peptides 1-40 or 1-42. Amyloid β peptides can associate intracellularly into dimers, higher order oligomers, and insoluble fibrils which are the major protein component of senile plaques that accumulate in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients. Amyloid β peptides enhance the hyperphosphorylation of Tau and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, another hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. Amyloid β also forms fibrils with ApoE and binds to the prion protein PrP(C). Amyloid β has showed diverse functions in brain. For example, it can directly disrupt the integrity of neuronal membranes. Amyloid β interaction with RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts) induces neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammatory activation of astrocytes and microglia. It also induces neuroinflammation through interactions with TLR2 (Toll-like receptor 2). Amyloid β binds and activates the nicotinic acetylcholine alpha 7 receptor, leading to neuroprotection, enhanced synaptic plasticity and memory formation, and the upregulation of acetylcholinesterase.