Data sheet
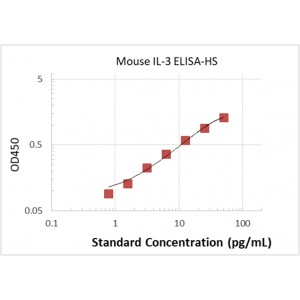
| Assay Range | 0.78 – 50 pg/mL |
| Background | IL-3 is produced as a monomer by activated T cells, monocytes/macrophages and stroma cells.Interleukin 3 stimulates the differentiation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells into myeloid progenitor cells or, with the addition of IL-7, into lymphoid progenitor cells. In addition, IL-3 stimulates proliferation of all cells in the myeloid lineage (granulocytes, monocytes, and dendritic cells), in conjunction with other cytokines, e.g., Erythropoietin (EPO), Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and IL-6. It is secreted by basophils and activated T cells to support growth and differentiation of T cells from the bone marrow in an immune response. Activated T cells can either induce their own proliferation and differentiation (autocrine signalling), or that of other T cells (paracrine signalling) – both involve IL-2 binding to the IL-2 receptor on T cells (upregulated upon cell activation, under the induction of macrophage-secreted IL-1). The human IL-3 gene encodes a protein 152 amino acids long, and the naturally occurring IL-3 is glycosylated. The human IL-3 gene is located on chromosome 5, only 9 kilobases from the GM-CSF gene, and its function is quite similar to GM-CSF. |
| Sample | 5-10 µL mouse serum/plasma |
| Alternate Names | IL3; IL-3; IL-3MGC79398; interleukin 3 (colony-stimulating factor, multiple); interleukin-3; Mast cell growth factor; mast-cell growth factor; MCGFMGC79399; MULTI-CSF; multilineage-colony-stimulating factor; Multipotential colony-stimulating factor; P-cell stimulating factor; |
| Gene ID | 16187 |
| UniProt ID | P01586 |
More info
Size
96T
Range
0.78 pg/mL-50 pg/mL
Sensitivity
0.26 pg/mL
Specificity
No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokine.
Storage
Store at 4 °C for frequent use, at -20 °C for infrequent use.
Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles (Shipped with wet ice.)
Expiration
6 months at 4 °C and 12 months at -20 °C.
Application
serum, body fluids, tissue lysate, cell culture supernates.
Kit Components
1. Lyophilized recombinant mouse IL-3 standard: 50 pg/tube-2.
2. One 96-well plate precoated with anti- mouse IL-3 antibody.
3. Sample diluent buffer: 12 ml x 2
4. Biotinylated anti- mouse IL-1a antibody: 60 µL, dilution 1:180.
5. Antibody diluent buffer: 12ml.
6. Strepavidin-HRP: 300µL, dilution 1:40.
7. Strepavidin-HRPdiluent buffer: 12ml.
8. Chromogen-A, 6 ml; Chromogen-B, 6 ml.
9. Stop Solution: 6 ml.