 View larger
View larger
Human Folate ELISA Kit
NR-R10222
Human Folate ELISA KitÂ
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Data sheet
| Background | "Folate" is the term used to name the many forms of the vitamin—namely folic acid and its congeners, including tetrahydrofolic acid (the activated form of the vitamin), methyltetrahydrofolate (the primary form found in the serum), methenyltetrahydrofolate, folinic acid, and folacin. Other names include vitamin B9, vitamin Bc, vitamin M, and pteroyl-L-glutamate. Folate is necessary for the production and maintenance of new cells, for DNA synthesis and RNA synthesis through methylation, and for preventing changes to DNA.It is especially important during periods of frequent cell division and growth, such as infancy and pregnancy. Folate deficiency hinders DNA synthesis and cell division, affecting hematopoietic cells and neoplasms the most because of their greater frequency of cell division. RNA transcription and subsequent protein synthesis are less affected by folate deficiency, as the mRNA can be recycled and used again (as opposed to DNA synthesis, where a new genomic copy must be created). Since folate deficiency limits cell division, erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells) is hindered. This leads to megaloblastic anemia, which is characterized by large, immature red blood cells. |
| Alternate Names | folic acid, folacin, vitamin B9 |
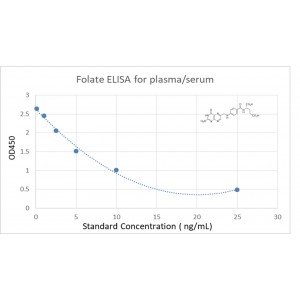
| Assay Type | Competitive ELISA |
| Kit Type | Colorimetric |
| Assay Time | 70 minutes |
| Sample Type | Serum, Plasma |
| Assay Range | 3.2 ng/ml- 13.7 ng/ml |
| Sensitivity | 0.5 ng/ml |
| Specificity | No cross-reactivity with Bilirubin, Biotin,Lipemia |
| Precision | Intra-Assay 6.7%; Inter-Assay 8.7% |
| Sample Volume | 50 uL |
| Dilution Factors | See manual |
| Storage | See manual |
More info
The kit is used to quantify Folate in human serum. This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Folate. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Folate and analogues was observed.